Cross-
Cutting
Research Area
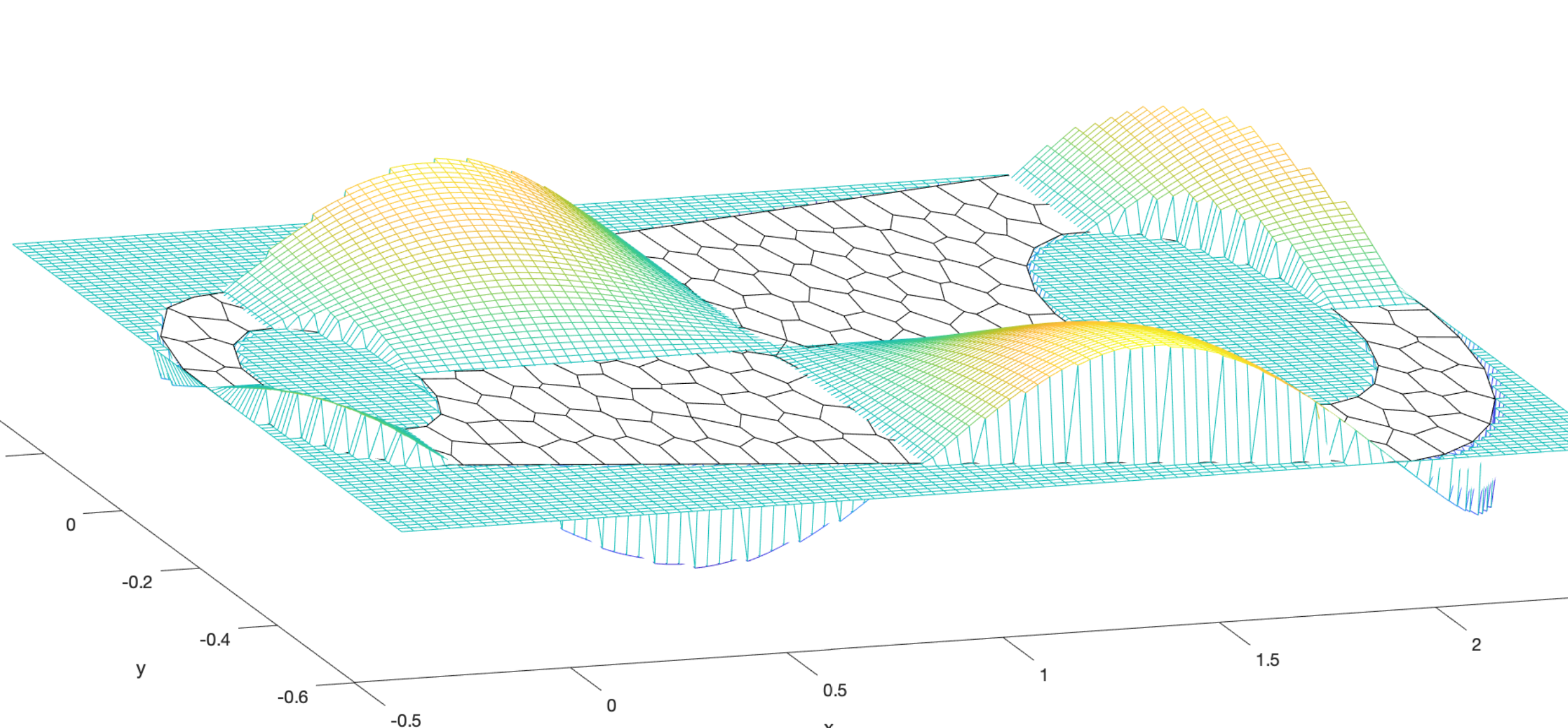
The study of algorithms for numerical approximation
Numerical Analysis is a branch of mathematics and computer science that creates, analyzes, and implements algorithms that use numerical approximation. The recent growth in computing power has revolutionized the use of mathematical modeling, and at the same time it revealed subtle and sometimes mysterious numerical issues. Questions addressed, for example, may concern accuracy and error estimation, stability of the model to small perturbations including rounding error, preservation of physical principles, multiscale modeling and model adaptivity, data assimilation and inverse modeling, predictive science, computational complexity, machine learning, computational efficiency, software, and computer hardware.
Numerical PDEs is the subset of numerical analysis concerned with the numerical approximation of partial differential equations (PDEs), integro-differential equations (IDEs), and optimization and control. Systems of PDEs and IDEs with inequality constraints underlie many if not most of the mathematical models arising in the natural and social sciences, engineering, medicine, and business.
Research is multifaceted, ranging from foundational advances in theory, methods and algorithms, to real-world impact in grand challenge problems. Some examples of current research areas include:
Finite element methods. The aim is to solve all kinds of PDEs efficiently and to within specified error bounds using unstructured, polyhedral, and refined computational meshes.

Discontinuous Galerkin (DG) and Discontinuous Petrov Galerkin (DPG) methods. These are special finite element methods, and the goal is to understand and exploit their many advantageous properties.

Isogeometric analysis. The vision is an integration of computational geometry and analysis, by unifying the disparate methods and data structures of Computer Aided Geometric Design (CAGD) and finite element analysis.
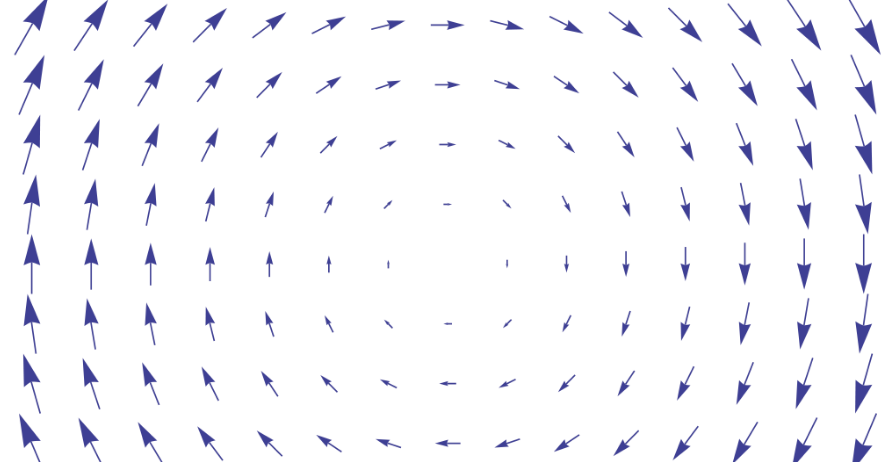
Approximation of div-curl PDE systems. These arise in many problems of mechanics and physics, such as those involving electromagnetism, acoustics, and diffusion. They have a precise mathematical structure, and the challenge is to preserve this structure within the numerical methods.

Fluid structure interaction (FSI) problems. These arise in many important applications, and involve complex numerical issues related to mechanical structures deforming within a fluid.

Hyperbolic conservation laws. These PDEs model, e.g., transport processes, fluid dynamics, and turbulence. The equations offer special challenges related to the interaction of numerics and physics, such as arise in the formation of shocks and dealing with nonuniqueness of solutions.

Boltzmann type equations and particle transport. Challenges include preservation of physics in numerical methods at quantum, kinetic, and fluid scales, and approximation of high-dimensional non-equilibrium statistical flows.
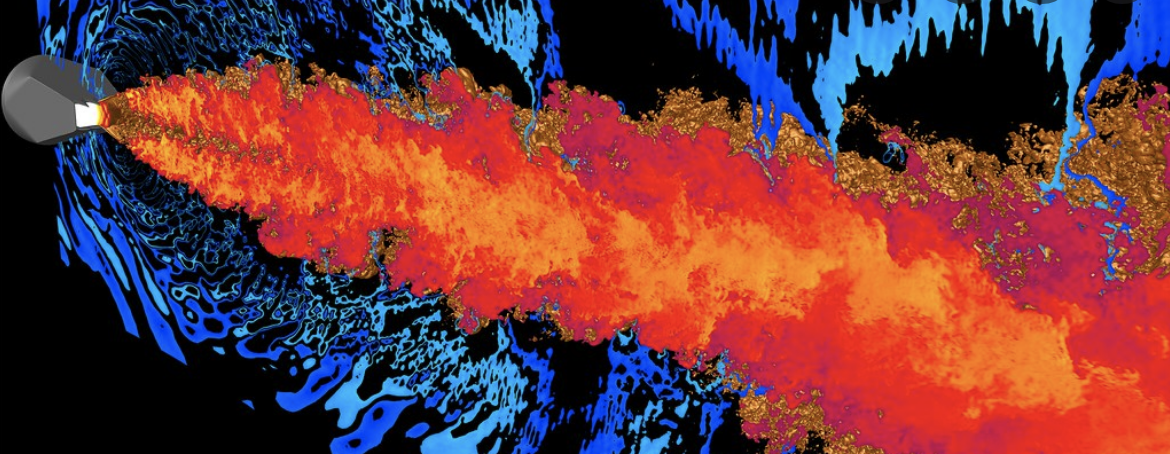
Multiphysics simulation. A complex system often contains many smaller, coupled subsystems. Solving them iteratively leads to possible nonconvergence of the overall problem and issues of propagation of errors between subsystems.
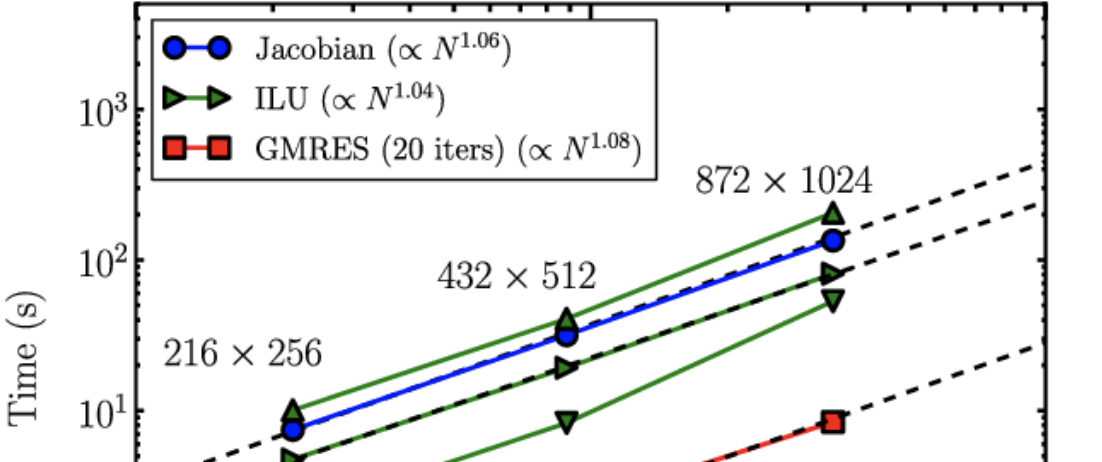
Solution of linear systems. Most numerical methods reduce at some level to very large systems of linear equations, and the overall computational cost is related most strongly to the time needed to solve these linear systems. Algorithms using direct, probabilistic, and iterative methods are explored in a massively parallel, high performance computational setting.
To learn more about projects and people in Numerical Analysis and Numerical PDEs, explore the centers and groups with research activities in this cross-cutting research area.

Profile
March 11, 2026
CSEM student Rodrigo José González Hernández shares his journey from his early beginnings in astronomy to his current research in kinetic theory.

News
April 24, 2025
The Frontiers in Computational Mathematics Conference celebrated Professor Bjorn Engquist’s 80th birthday and his impact on numerical analysis, mentorship, and interdisciplinary research. The event brought together global scholars and students to explore the future of computational mathematics in an era increasingly shaped by AI.

Profile
Feb. 21, 2025
Joe Kileel, Principal Faculty at the Oden Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences, and mathematics professor was awarded a Sloan Fellowship in February 2025.